We’re all aware of black hat SEO practises and the negative impact they have on page rankings when Google detects them. If you run an SEO agency, you should be aware of Google’s manual penalty if it discovers you using black hat SEO tactics.
As a result, firms are shifting their focus away from black hat SEO and toward white hat and technical SEO. However, competitors have devised a new tactic to undermine your efforts and jeopardise your ranks. Negative SEO is what it’s called, and it may seriously hurt your rankings.
What is Negative SEO?

Negative SEO refers to approaches and methods targeted at destroying competitors’ ranks and reducing their organic traffic. Businesses use black hat SEO practises on their competitors’ websites with the purpose of sabotaging their SEO efforts.
Let’s look at how competitors do it and how to protect yourself from negative SEO attacks.
Types of Negative SEO
Negative SEO has progressed over time. It started with backlinks, where site owners listed links to bad, toxic websites that their competitors had. As a result, there were a lot of harmful spammy links, which could be fixed by putting them in the disavow file.
In 2020, however, attackers will have several options for performing negative SEO. In the current situation, it is far more dangerous and difficult to identify.
Attackers utilise both off-page and on-page SEO approaches to harm their competitors’ rankings and organic traffic. To keep you informed and secure from such attacks, we’ve created a list of negative SEO tactics.
Negative Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO tactics are used by attackers to sabotage a website’s rankings. They are mostly concerned with generating poor backlinks to the website.

Link Farming
This is a well-known example of black hat SEO. Allow me to provide an overview of link farms. A link farm is a collection of related websites that are linked together. These websites exist solely to provide hyperlinks to promote specific pages on your website.
Link farms were employed by site owners to boost their page rank and gain strong SERP rankings. However, Google’s Penguin algorithm severely penalised such sites in 2012. The end of link farms had arrived.
This technique is used by attackers to send a huge number of spammy links from link farms to the target website. This action is detected by Google, resulting in a sharp reduction in the targeted website’s ranks.
Tips to recover from this
Let’s be honest about it! We have no control over the abrupt backlinks that our competitors are sending. However, checking backlinks on a frequent basis to detect malicious connections is a smart practise.
You could use the SEMrush tool to perform a backlink audit.
Keep an eye out for backlinks with a high poisonous score and make sure they’re included to the disavow list. After that, you must submit the disavow list to Google using the search panel.
As a result, Google will delink your website from these bogus links. This will aid in the recovery of your website and the retention of keyword ranks.
Bad Reviews
This is a whole new level of enmity. Competitors go so far as to form alliances with individuals and organisations in order to generate false reviews about your company.
This has a substantial impact on your website’s SERP ranking because it provides Google a negative picture of your business.
Your local SEO rankings are also affected by bad 1-star reviews. This has the potential to be quite dangerous. You may begin to lose your customers’ trust in your brand.
How to recover from this
When it comes to bogus reviews, Google is really tough. They also have a policy prohibiting the use of sponsored reviews. You may evaluate the evaluations that your firm is receiving by going to your Google My Business account. Keep an eye out for any illogical reviews.
Once you’ve discovered such compensated evaluations, make a note of them. You will be required to fill out a brief report, after which Google will delete the bogus reviews from your listings.
Scraping Content
Scraping (copying) your website content and distributing it on multiple websites is a black hat SEO strategy. Duplicate content is the outcome of this. Site owners utilised this strategy to rank better in the SERP in the past and got away with it.
Then there was the Panda algorithm upgrade, which did a good job of detecting duplicate content. Sites that used this method were harshly penalised.
Attackers take advantage of this. They duplicate stuff from one website and post it on several others.
Google may index these pages with copied content first in some cases. The original page will be de-indexed, which will have an influence on their rankings.
How to recover from this
This scraping technique is used by a lot of rivals. Many technologies are available to help identify scraped content on the internet. Copyscape is an example of such a programme. It aids in the discovery of competitors’ scrapped copies of a certain page. Using a tool like Quetext to discover duplicate content is another option. This displays which pages include content that is comparable to that of the original page.
If you find scraped pages on your site, contact the page’s webmaster to get the content removed from the duplicated site. If it doesn’t work, you can contact Google and tell them about the scraped content. This copyright infringement form can be filled out.
MUST READ: What are Backlinks and Why are They Important in 2021?
Pogo Sticking
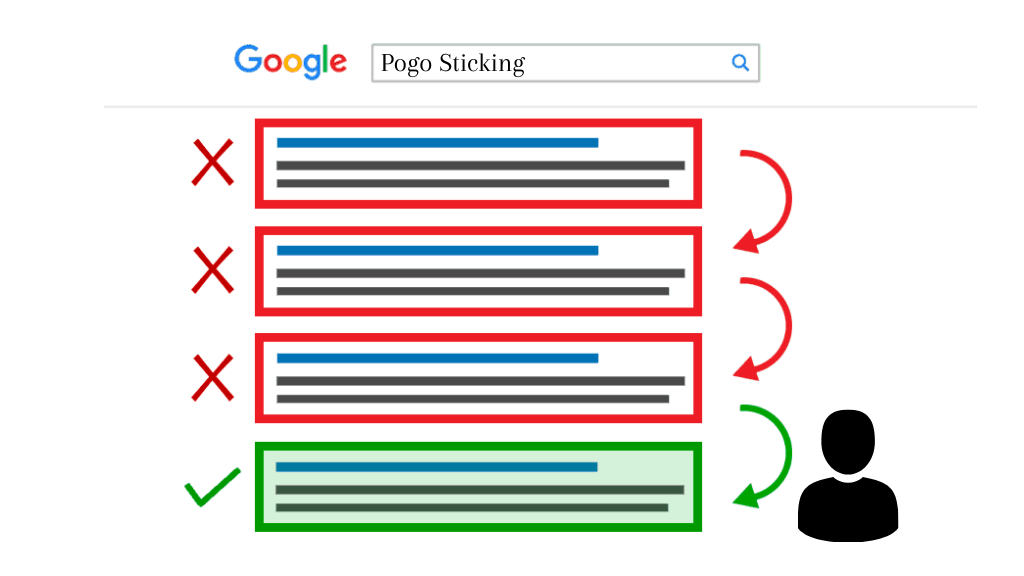
When people click on a page in the SERP, don’t find what they’re looking for, and quit the page, this is known as pogo sticking. This typically occurs when a person uses Google to search for a phrase and is directed to a website that does not answer his question. This pogo-sticking is tracked by Google. For Google, this indicates that the website is not a suitable SERP result. As a result, the website’s ranking suffers.
Attackers utilise customised bots to search the search engine for terms that can boost your website’s ranking. These bots then visit your website and then swiftly go. Pogo-sticking is demonstrated in this way. This has a significant impact on your website’s rating and traffic.
How to recover from this
Keep an eye on the most crucial pages that your website ranks for. In Google Analytics, keep an eye out for critical indicators for these pages.
Go to Site Content -> Landing Pages in Google Analytics. Keep an eye on the “Bounce Rate.” Examine the “Bounce Rate” of your web page/s to see if there is any strange behaviour.
This will let you know if your site has been targeted by this bad SEO practise.
Negative On-Page SEO
Assailants change on-page features of your website, resulting in catastrophic consequences. This eventually results in a decline in traffic and rankings.

Making changes in Content or Code
This necessitates a high level of hacking expertise. Competitors, on the other hand, can go to extremes if you are a hostile rival. The attacker tries to uncover any security weaknesses in the backend of your website and exploit them. This emphasises the need of using an SSL HTTPS certificate.
If your security is breached, the attacker will have access to the code and content of your website. They can then change the coding so that you view one version of the page while your users see something entirely different. Your website’s ranking will suffer as a result of this.
MUST READ: SEO Testing: All You Need to Know
How to recover from this
Always keep your backend software, as well as all of the classes and elements utilised to create your website, up to date. It’s also critical to write a script that backs up your web pages. If your website gets hacked, it will be much easier to restore it to a prior backup. Conduct frequent SEO site audits and keep your security certificates up to current. Purchase an SSL HTTPS certificate that is legitimate.
This will both safeguard your website from hackers and improve its rating (HTTPS is a ranking factor).
Intentional DDoS Attacks
A DDoS (Distributed Denial-of-Service) attack is when an attacker sends a significant amount of traffic to your website. This causes the server to crash, rendering your website inaccessible. Users will have a difficult time navigating your website.
DDoS assaults are used by attackers to dramatically increase the strain on your server. The user’s experience with the UI is hampered as a result of this. Many people may be unable to access your website. Furthermore, the Google spider will be unable to crawl your web pages.
This reduces your crawl budget, and Google will stop crawling and indexing your content.
How to recover from this
Monitor the speed of your website on a regular basis. Keep a watch on the Google Page Speed Insights metrics for your website’s critical pages, such as FCP (First Contentful Paint), FID (First Input Delay), and Speed Index.
Check your server logs if your web pages are slowing down without any changes to the code. The log files will assist you in determining the exact source of the increased server load. Once you’ve identified the source, you can use the robots.txt file to stop these crawlers.
MUST READ: How to do Website Speed Optimization in 2021
Delete your site entirely from Google
Isn’t it ridiculous? This, however, can happen to your website. This might be done by a former employee who now works for one of your competitors.
When an ex-employee still has access to the accounts, situations like this can happen. Ex-employees (now working for your competitors) may alter your search console and remove your website from Google’s index entirely.
He can also prevent all spiders from crawling your websites, including the Google Bot.
How to recover from this
Before they depart the company, delete all of your ex-accounts. employee’s Remove all access and permissions as well. This assures that the employee has no control over your property.
If you suspect manipulation, go to your search console and click on the “Removals” button as soon as possible. Check to see if there are any new requests. All of the requests will be removed if you quickly click “Cancel.”
Check your robots.txt file as well to see if any crawling bots have been blocked.
Conclusion
To improve the website, different types of SEO strategies are used. Where there is good, however, there is also evil.
Negative SEO practises are a disgrace to the SEO profession, yet they do exist. This emphasises the importance of doing website audits on a regular basis. Follow a rigorous SEO audit checklist to ensure that all of your critical on-page and off-page SEO elements are in good working order.
This will ensure that you are informed of any negative SEO attacks launched by your competition.
If you discover such attacks too late and Google has already imposed a manual penalty, we recommend contacting an SEO firm that specialises in Google penalty recovery. This will assist you in regaining your website’s search engine rankings and traffic.
Let us know if you’ve been a victim of negative SEO attacks and how you rebounded in the comments