The organic channel contributes the greatest traffic to the majority of websites. The organic route has the highest conversion rate. This increases businesses’ reliance on Google. Even a small rise in Google ranking for a few keywords might assist raise the amount of leads and consequently the revenue.
Some SEO practitioners may manipulate the search index to gain better and faster results through the organic channel by either over-optimizing their website or utilizing some black-hat SEO tactics. And do you want to guess what Google does with them? A Google penalty that lowers the value of their website.
What is Google Penalty?
It’s important not to mix up Google algorithm updates and Google Penalty. A Google penalty is a human action performed by Google if your website does not follow Google’s webmaster standards, whereas an algorithm change affects Google’s search results.
Google Penalties are extremely comparable to penalties in sports. They’re mostly intended to punish websites that have broken the law. These penalties aren’t always applied manually, and they may affect websites created by people who had no idea what they were doing wrong, but they can nevertheless have a significant influence on a site’s search results—and beyond.

A Google Penalty means trouble
A Google penalty means that your site is no longer listed in search results or that your rating for your chosen keywords has dropped. Your target audience will be unable to find you if your site receives a Google penalty. When you become invisible to your target audience, your traffic and, as a result, your revenue decreases.
Any website could be affected. A Google penalty can occur from genuine and well-intentioned efforts to increase your site’s ranking. However, once you’ve received a Google penalty, regaining your good rating and getting back into Google’s good graces isn’t easy.
Digital Universe can assist you in regaining your Google ranking. We have a specialized staff that will review your site and make the required improvements to get you back to the top of the search engine results. You haven’t gotten a Google penalty yet, but you want to be safe. Our skilled internet marketers keep up with Google’s ever-changing algorithms to ensure that your site is always in good standing and never in danger of being penalized.
We know what search engines prefer to see as a leading Google penalty repair provider. Our penalty recovery solution is designed to bring you back into good standing with Google so that your website can appear in search results and your business can continue to thrive.
Why do sites get a Google Penalty?
Google’s job is to deliver the most relevant search results. Any website that tries to influence search results, according to Google, is hurting the Google product. Would Google still be Google if it returned useless results or provided a poor experience to its users?
A Google penalty is the result of Google’s highly sophisticated, ever-changing system for crawling and inspecting webpages. While there are some activities that can result in quick penalties from a Google employee, there are others that aren’t publicly announced, or some that can result in a gradual drop in rankings. This is to keep Google safe from malicious websites.
The list of Google penalty triggers is long, but it’s easy to summaries: penalties are triggered by any action taken by a website to deceive a search engine or degrade the user experience in some way.
List of Google Penalty or Manual action by Google
User-generated spam
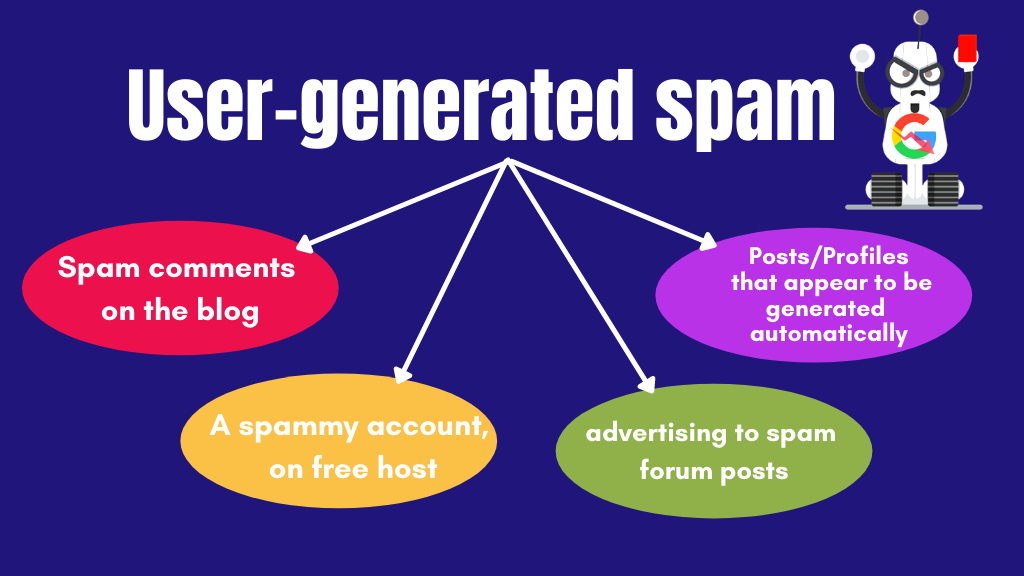
This manual penalty is the result of malicious visitors or users attempting to spam the website with irrelevant links or information, rather than the site owner violating webmaster standards. This penalty is more likely to affect websites that accept user-generated content. Here are a few instances of spammy content created by website visitors:
- Spam comments on the blog.
- A spammy account, on free hosts,
- Using content that appears to be an advertising to spam forum posts.
- Posts/Profiles that appear to be generated automatically
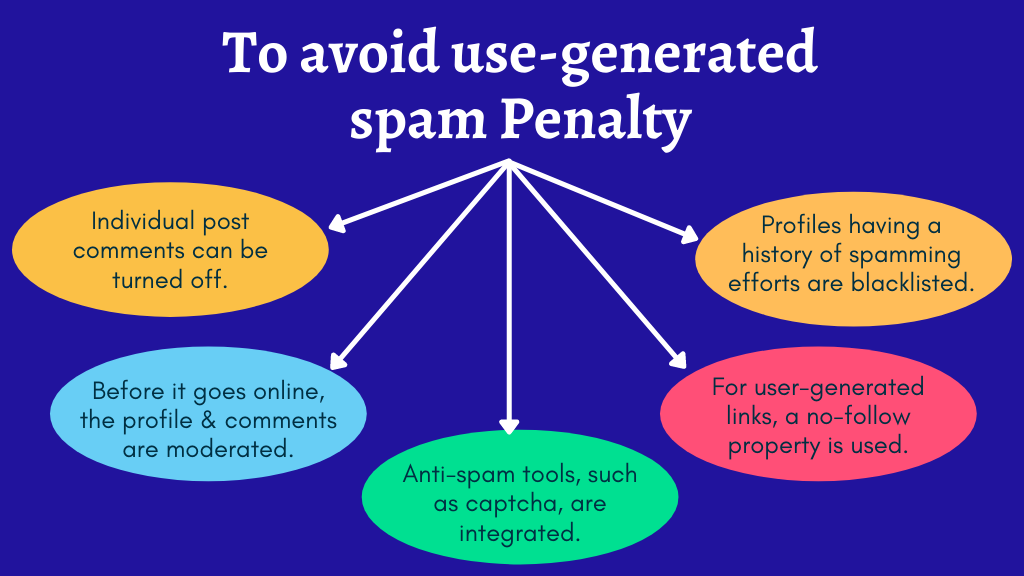
It is vital to keep an eye on your website for the types of spam described above that malevolent visitors may attempt to send. Here are a few pointers to help you avoid this penalty.
- Individual post comments can be turned off.
- Before it goes online, the profile and comments are moderated.
- Anti-spam tools, such as captcha, are integrated.
- For user-generated links, a no-follow property is used.
- Profiles having a history of spamming efforts are blacklisted.
If you receive this penalty, you must identify and remove all spammy content from your website. You can use Google Search Console to submit a reconsideration request after you’re satisfied the website is spam-free.
Spammy hosting service
This Google penalty is the result of your hosting provider being spammed by creating websites that blatantly violate the webmaster standards. This is a typical issue with free web hosting services.
If you use a free hosting service and Google determines that a large number of the websites hosted by this service provider are spammy, a manual action against the service provider can be performed. All hosted websites will be subject to a manual penalty as a result of this.
It is critical to pick a reputable hosting service provider to host your website. It is also recommended that if you are subjected to this penalty, you replace your hosting service provider.

Structured data issue
This Google penalty will be applied if there is a mismatch between the content served and the structured markup used on the website.
Additionally, if your website violates Google’s structured data requirements, you will be penalised. Before going live with the code modifications, make sure you follow the structured data markup requirements and test the markup with the structured data testing tool.
Unnatural links to your website
Some SEO professionals resort to mass link building, manipulative link building, or link trades in order to outrank competition. This is an attempt by Google to tamper with their search results. As a result, such behavior is classified as unnatural. The following are some of the things you should keep in mind to avoid this penalty:
- Avoid link-exchange schemes at all costs.
- Avoid using the precise keyword-rich anchor text when linking at scale.
- Through the search console, keep an eye on external links and try to remove or disavow any spammy connections you see.
- Avoid using the same keyword-rich anchor text in successive guest posts.
- There is a fair balance of no-follow and do-follow links.
Unnatural links from your website
This penalty occurs when our outbound link profile is unnatural. It’s identical to the previous penalty, with the exception that this one applies to outgoing links, whereas the previous one applies to links generated for our website on other sites. Linking to unrelated domains, excessive link exchange, and link buying and selling should all be avoided.
Thin Content
It is critical to ensure that the material on your website is useful to users and does not contain spam. A content penalty will be applied if Google identifies several instances of low-quality pages on your website. The following are some examples of thin content:
- Content that is generated automatically
- Affiliate pages are pages established solely to promote affiliate links.
- Scraped content or low-quality guest blog articles are two examples of low-quality guest blog posts.
A content audit can help you avoid the penalty by removing low-quality and thin information from your website on a regular basis.

Cloaking
This penalty might be imposed if your website presents distinct content to consumers and search engines. Both people and Google bots should see the same content, according to Google. Here’s a video that explains what cloaking is and shows some examples.
Use the URL Inspection Tool to observe how the Google bot sees your page and make sure the content is similar to what a human visitor sees.
How can I recover from a Google Penalty?
It’s not always simple to get rid of a Google penalty. It’s important to understand that there are two types of penalties: manual and algorithmic penalties.
A Google employee is the one who imposes the manual penalty. When your website is determined to be in violation of Google’s Terms of Service, you’ll most likely receive one. A virus infection, cloaking, redirection, or purchasing links are all examples of this. Before an automatic penalty is imposed, you must request that Google reindex your website—that is, return it to the search engine results—before an automatic penalty is imposed.
On the other hand, an algorithmic penalty is imposed automatically, without the need for Google to intervene. These are frequently the result of an algorithm modification intended to priorities valuable websites over those with inferior content or relevance.
Websites with thin or duplicate content, keyword-stuffed copy, slow loading speeds, or a lack of incoming links may be penalized by algorithmic penalties like as Panda, Penguin, and Hummingbird. You will still rank in search with this penalty, but it will most likely be significantly lower.
You can read our expert’s guide to penalty recovery, which is an in-depth guide to this process, if you want to learn more about diagnosing and removing your penalty. It will assist you in identifying your exact penalty and determining the steps necessary to erase it.
Do you require assistance? Digital Universe’s Google penalty recovery services may be the greatest option for you if you’re not sure what you’re doing or where to begin. Our expert team can locate and remove your penalty, letting you to concentrate on operating your business rather than reviewing links or rewriting material.
Conclusion
Being charged with a Google manual penalty will lower the value of your website in Google searches, as well as reduce organic visitors and hence revenue. As a result, it’s critical to make sure your website follows the webmaster rules.
If you are penalised, however, you should not be alarmed because you may troubleshoot the problem and submit a reconsideration request to Google through the search panel. If you’re having trouble recovering from the penalty, we’d be happy to assist you with our Google penalty recovery services.
Read : How to do Keyword Research in SEO
Google Penalties: How to Find, Fix, and Avoid

Every website owner wants their site to rank higher in search engines and have more online visibility in order to attract more visitors.
Using unauthentic approaches and spamming activities, on the other hand, may have the opposite effect, wreaking devastation on your website.
Yes, when the bots discover any infringement of the webmaster standards, Google has the right to penalise websites.
Based on the manual spam acts discovered, these penalties range from lowering the search engine ranking of the corresponding website to eliminating it from the search engine results pages.
This is why earning Google penalties is every webmaster’s worst nightmare.
Since 2012, Google has spoken with webmasters through the Google Search Console. Google uses this service to notify websites about issues that are likely to have a detrimental impact on their search visibility.
These signals are referred to as “warnings” by Google, and webmasters are encouraged to analyse and respond to them as soon as possible.
So, as a website owner, what can you do about it? The solution is straightforward. You must gain a broader understanding of Google penalties.
Yes, you can only avoid a problem if you understand where and how it arises. Or, in the worst-case situation, figure out how to cure a Google penalty if one is imposed on your website.
ALSO READ: Google Answer Box: Why It Matters and How to Optimize it.
Types of Google Penalties

Google penalties are divided into two types: algorithmic penalties and manual penalties. Let’s break them down one by one.
1. Algorithmic Penalties
Google algorithms are a complicated system that aims to get relevant information from its search index and present the best results to the user in order to answer the query.
Google’s algorithms are updated on a regular basis to improve the quality of search results and thus the user experience. The fact that Google’s algorithm upgrades are unpredictable adds to the complexity for website owners and digital marketers.
When an algorithm is updated, websites or individual landing pages that do not meet the specifications defined in the most recent algorithmic tweak are frequently penalised.
The term “algorithmic penalty” refers to a modification in Google’s algorithms that impacts the ranks of websites that Google believes do not meet its requirements.
Is an algorithmic penalty irreversible? Definitely not.
If an algorithm update has had a negative influence on your website, that doesn’t imply you can’t recover.
You can improve your website’s search engine rankings by taking reasonable measures, identifying and fixing the flaws that produced the negative impact, and revamping your website with high-quality, user-engaging content while avoiding black hat methods.
2. Manual Actions
Since the inception of search engines, people have experimented with various methods to deceive them and improve their search engine ranks.
This has an impact on searches since useful search queries are buried beneath a slew of irrelevant results.
This is why Google has been fighting spammers from its inception in order to provide users with a better search experience.
The Google webspam team periodically checks to see if websites are following the Google webmaster quality criteria. In the event of a violation, the webspam team can manually block certain websites, and the website owner is notified via the Google search panel.
Simply defined, a manual penalty occurs when a Google employee examines your website and determines that it should be delisted from Google because certain standards have not been followed.
So, how do you determine whether your website has been penalised manually?
Team Google will send you an email notification about the problem, and it will also appear in Google Console when you log in. You’ll notice a notification with a green tick mark at the top of the report notifying you about it.
You can make a reconsideration request once you’ve fixed the problem on your end.
Your request for reconsideration will be carefully reviewed by the Google webspam team. The ban on your website will be lifted once they verify that you have done the necessary actions to comply with Google’s webmaster quality requirements.
Reconsideration requests can take a week or two to be processed. When Google receives your request and completes the evaluation, you will be notified by email.
Google does a variety of manual operations, and this page will attempt to explain each one in depth. We’ll also talk you how to get out of these fines.
The Complete List of Google Penalties and How to Recover

Cloaking and/or Sneaky Redirects
Cloaking is the process of providing distinct pages to the search engine and the user in response to a certain query. This is a breach of the webmaster guidelines, and as a result, a manual penalty will be applied.
There are two types of this penalty. Partial matches, for example, can effect specific areas of your website, such as individual landing pages. Two, site-wide matches that can cause the entire website to crash.
How to Fix?
Fetch as Google in Google Search Console by going to Crawl > Fetch as Google. You’ll be able to identify the parts of your website landing pages that are affected this manner.
Compare the content retrieved by Google with the parts of your website’s content that are untouched.
Determine the discrepancy and rework the affected portions until they are consistent with the unaffected content.
Getting sent to a page that is irrelevant to the query is something neither Google nor the user enjoys. As a result, look for any current redirects and remove those that take users to a different page.
You can make a reconsideration request whenever you believe all of the necessary adjustments have been made.
Cloaking: First Click Free Violation
Google’s First Click Free policy prohibits websites from requiring users to register, log in, or subscribe in order to view their content.
This is another sort of masking that can result in Google penalties for your website.
This penalty, like the last one, comes in two flavours: partial matches that affect specific portions of the website and site-wide matches that affect the entire website.
How to Fix?
To get rid of the penalty, make sure that the material displayed to Google and the users who come from Google services are the same.
Once you’ve resolved the concerns, you can file a reconsideration request to Google.
Cloaked Images
Do you believe that cloaking solely pertains to the content of your website? If you answered yes, you are mistaken.
Cloaking also applies to photographs.
When another image overshadows it or users are routed to other irrelevant pages away from the corresponding image, Google considers it cloaked.
How to Fix?
To prevent this penalty, you must make sure that Google and your visitors see the same image.
You can submit a reconsideration request once you’ve removed all potentially veiled photos from your website and replaced them with the correct ones.
Hacked Site
In the digital world, hacking is unavoidable. Without your knowledge, hackers may hijack your website and inject malicious content or links into your content management system. Because these bogus links are frequently veiled, it is difficult to detect them.
When Google detects such sites, it displays a “the site is hacked” message on relevant Google search results pages. This may cause people to leave your site, as well as a drop in its search engine rating.
ALSO READ: What is ROAS – Return on Advertising Spends?
How to Fix?
When you discover that your website has been hacked, the best thing you can do is establish measures to prevent further damage. To do so, contact your web host to isolate your website and request assistance.
Using Google Search Console, determine the degree of the malware’s impact. Check the free google malware checker here
Now you must get to the root of the problem in order to solve it and prevent it from happening again. Yes, conduct a thorough examination of your website to uncover the weak points via which hackers gained access to your data.
Based on your findings, make changes to your website to fortify it and prevent future attacks. At this stage, make a point of having a backup of your website’s data and bolstering it with additional security features.
Request a review from Google on a regular basis to remove the “hacked” designation from your site.
Hidden Text / Keyword Stuffing
One of the most important Google ranking variables is content quality. Stuffing keywords into your website’s content in the hopes of increasing visibility and search engine rankings only serve to backfire.
Yes, if hidden text or crammed keywords are discovered in your content, Google has the right to penalise your website.
This penalty can be in the form of partial matches that affect only parts of the website or site-wide matches that have a negative impact on the entire website.
How to Fix?
To locate your website landing pages with damaged areas, go to Google Search Console > Crawl > Fetch as Google.
Using CSS positioning, find related text and uncover hidden material. Once you’ve discovered the hidden information, you can either delete it or restyle it to make it more visible to your visitors.
Similarly, look for crammed keywords and eliminate any instances of them from the material that are unnecessary or irrelevant.
Remove redundant content from title tags and alt texts next.
After you’ve completed all of these steps, contact Google and ask for a reconsideration.
Pure Spam
A website that uses spammy strategies and actions to improve its search engine ranks receives the pure spam penalty.
Black hat methods such as cloaking, content scraping, and others that violate Google Webmaster Guidelines are considered pure spam.
Depending on the severity of the spam, this penalty can be partial matches or site-wide matches.
How to Fix?
To avoid the pure spam penalty, you must remove all spammy actions associated with your website, preserve authenticity, and then request a reconsideration.
Spammy Free Hosts

Have you come across any free hosting options? It’s supposed to be spam. Practically speaking, nothing of great quality is free.
The free spamming hosts just serve to assault your website’s users with unrelated advertisements.
This means that once these free spammy hosting services have been deducted, the Google webspam team will take manual action against them.
How to Fix?
Switching to a reliable and authentic web hosting service is the quickest and easiest approach to solve this problem.
Once you’ve chosen a reputable hosting service, you may ask Google to re-evaluate your website and lift the penalty.
Some premium Web Hosting providers
Spammy Structured Markup
Structured markup, also known as schema markup, is a set of codes that you use to structure the content of your website so that Google can crawl and index it more rapidly.
The inclusion of spammy structured markup, on the other hand, can lead to irrelevant or deceptive content. Such deceptive tactics frequently backfire, with severe consequences for your website.
Will Google penalise for spammy schema? Yes, Google will penalise your website if it discovers spammy schema markup on it, as this isn’t a fair practice.
How to Fix?
This problem can be resolved by upgrading your schema markup and deleting the spammy elements.
You can submit a reconsideration request to Google once you’ve made the necessary changes.
Thin Content

When your website provides content that is of little or no value to the user, you will be penalised.
Content plagiarised from other websites, spun content, low-quality guest articles, auto-generated content, and other forms of thin content are all examples of thin content.
While Google promotes getting the greatest possible result for every query, it’s no surprise that web pages that can’t meet that standard are penalised.Depending on the amount of thin content published on your website, this penalty applies to partial matches or site-wide content.
What is the best way to fix it?
Remove any content that has been spun or generated automatically from your website. In the same way, keep an eye out for duplicate content and rework it to make it more appealing.
Identify affiliate pages on your site and eliminate them. If you want to keep these affiliate pages on your site, make sure they have enough weight to give your users extra value.
The likelihood of duplicate material on your website might be increased by using doorway pages. As a result, make it a point to get rid of them.
Once you’ve resolved these concerns, submit a reconsideration request to Google.
Unnatural Backlinks

One of the most effective techniques to boost your website’s Google rating is to build backlinks to it. However, if you perform link building incorrectly, the penalties will be severe.
When you generate links from or to your website that aren’t natural, your website will be penalised by Google. It’s because these links are used to manipulate search engine rankings, something Google doesn’t appreciate.
What is the best way to fix it?
Google Console allows you to download all of your website’s backlinks.
Now double-check them to determine if any of them do not follow Google’s criteria. If this is the case, you may either remove them or make them no-follow attributes. This isn’t only for links to your site that aren’t natural. This process can also be used to remove artificial links from your website to other websites.
Switching them to no-follow is proving to be challenging. Don’t be concerned. In some circumstances, this occurs. You can still remove those links from your website to get the ban lifted.
You can submit a reconsideration request to Google once you’ve resolved these issues.
Expired Jobs
If you have job postings or advertisements on your website, please be sure to remove them as soon as they expire.
This is due to the fact that posting expired jobs results in a bad user experience, which Google disapproves of. The search engine, on the other hand, aims to send consumers to areas where they can find what they’re looking for.
As a result, expired job postings may result in a Google manual penalty.
What is the best way to fix it?
The first step is to delete the schema markup for job postings from your website. The user will be forwarded to the 404 code, which indicates that the job posting does not exist.
Second, provide a no-index meta tag on the page to tell the search engine not to index it when it crawls your site.
Submit a Google reconsideration request now.
Conclusion
Google strives to give users the greatest possible experience by leading them to the most relevant pages and thereby answering all of their questions.
Regardless of how frequently Google’s algorithms and manual actions are updated, the goal in every iteration is to improve the user experience.
Given the circumstances, you can avoid fines and low search engine rankings by designing your website with the user in mind. Google likes your website if consumers like it.
Your website will be trouble-free if you remember this every step of the way while also learning how to resolve unintended fines.